There are 4 main factors to assess diamonds, commonly known as the 4C`s (Color, Cut, Clarity and Carat) color is considered most significant. Hence, when it comes to fancy colored diamonds, the diamond’s color is the most crucial factor.
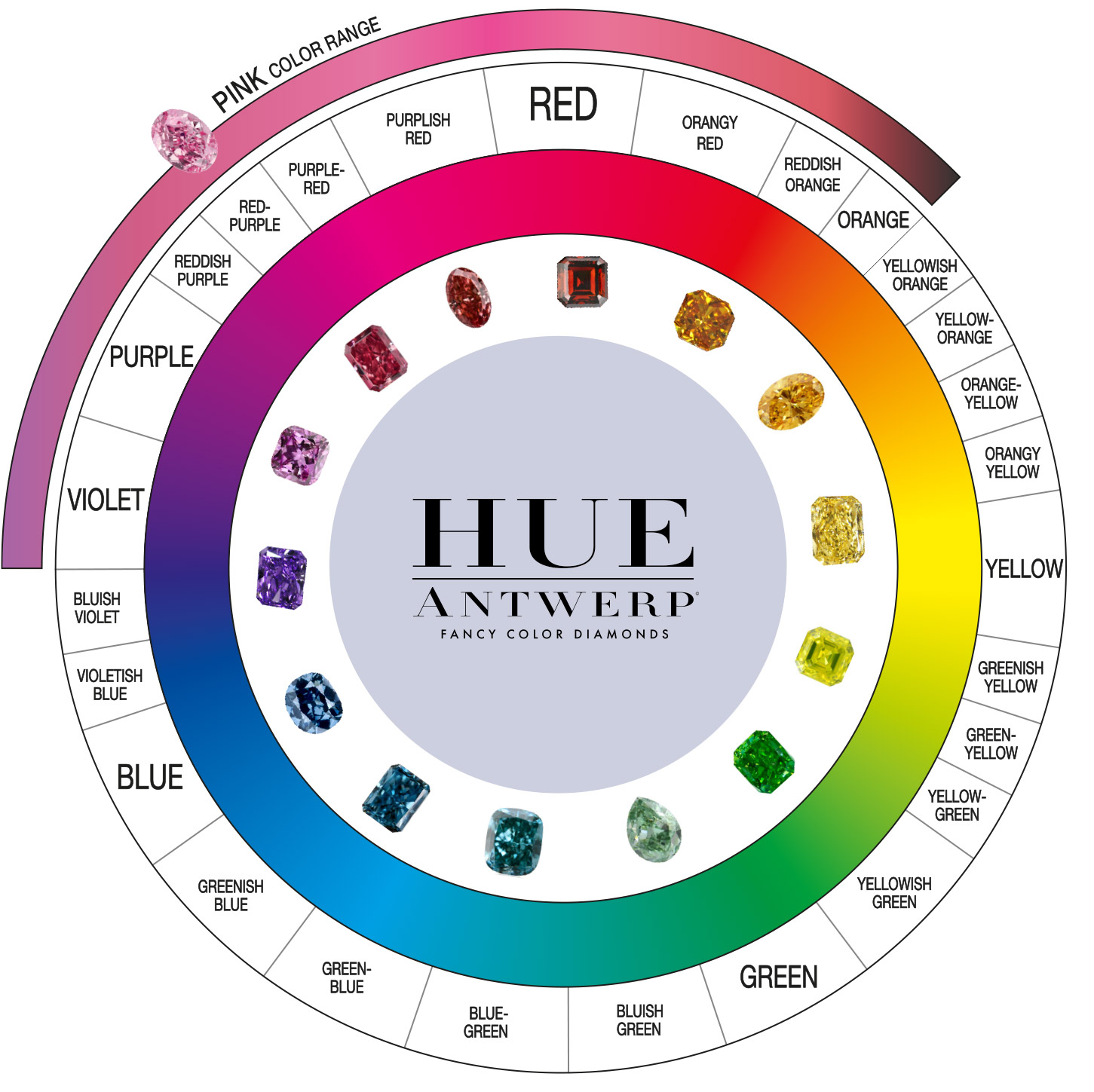
Color
With Fancy Color Diamonds, the crucial defining importance of Color and Intensity are used to assess the color of the stones using hue, tone, and saturation:
- The hue is the tint of color(s) present in the stone.
- The tone is the lightness or darkness of the color. The higher the tone, the darker the color.
- The saturation is the strength or purity of the colors and recognized as Intensity.
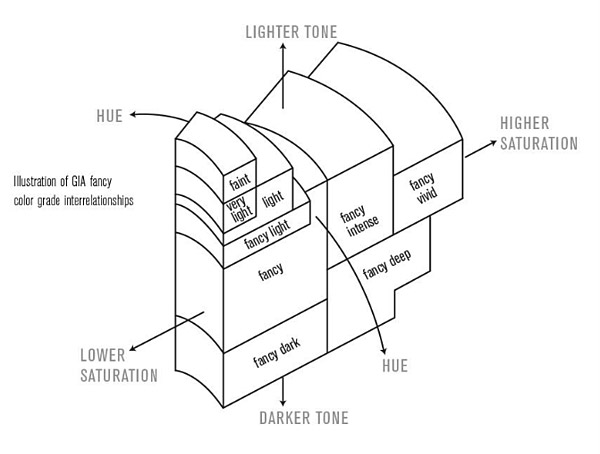
9 Intensity Grades
Broken down by nine Intensity Grades and the result of rarity, the value of the diamond increases through the intensity scale, with the rarest and most expensive being colors that receive the Fancy Vivid designation.
- Faint
- Very Light
- Light
- Fancy Light
- Fancy
- Fancy Intense
- Fancy Vivid
- Fancy Deep
- Fancy Dark
Cut
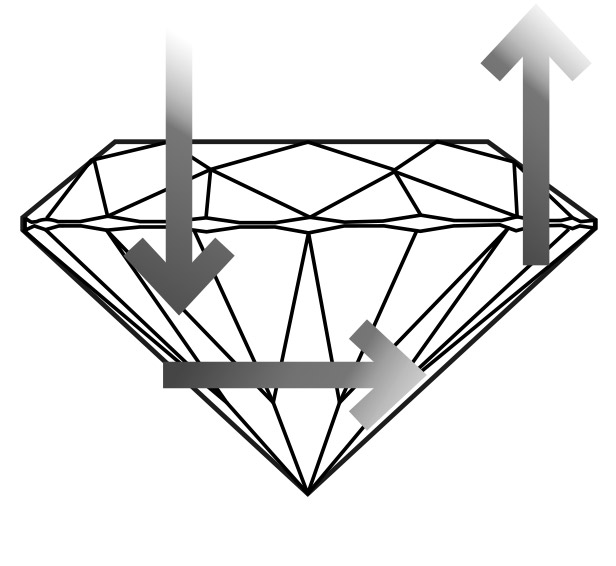
The cut of a diamond is often considered one of its most essential qualities. However, an expert diamond cutter’s patience, skill, and experience to sculpt a perfectly proportioned diamond, as inaccuracy, will affect its refraction or internal light performance.
A diamond’s cut refers to the quality of each tiny surface, called a facet. A well-cut diamond will have carefully crafted and positioned facets in areas known as the crown, girdle and pavilion. The facets are polished to sizes and angle with mathematical precision to maximise the diamond’s ability to reflect and return light to the viewer. With a descriptive phrase as a diamond’s ‘life’.
Cut within a Range Diamonds are given a cut classification as per below:
Excellent: Well proportioned, distributing light evenly through the diamond, this is the highest cut grade.
Very Good: Most of the light reflected through the crown, or the top, of the diamond.
Good: A diamond with a good cut will still reflect a good deal of light, but will not appear as brilliant as a higher cut grade.
Fair: Fair-cut diamonds will not display the correct proportions, which will cause a loss of light at the bottom of the diamond, appearing darker than higher cut grades.
Poor: Poor cut diamonds are the lowest cut grade, and often appear dull and lifeless.
Excellent Cut
Poor Cut
Very Poor Cut
Clarity
The clarity grade describes the number of imperfections found inside a diamond under a 10X magnification. Although a stone’s clarity is an important characteristic and will significantly affect the cost, it is not considered critical that the diamond be clear of inclusions, as Fancy Color Diamonds are extremely rare. Furthermore, some inclusions are far more challenging to see with the naked eye due to the colour.
The various levels of clarity in the GIA clarity scale for both white and color diamonds are defined below:
Carat
In the ancient world, carob seeds were a reference used for the weight of a diamond. However, weighing diamonds has become much more precise since today we measure a diamond’s weight in carats. One carat is equal to .2 grams and is divided into 100 points. Therefore, a half-carat, or .50 carat diamond, is also known as a 50 points diamond.
Carat is usually mistaken for a measure of size, when it is a measure of weight. Carat weight means the actual weight of the stone.